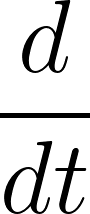"""
nbkode.core
~~~~~~~~~~~
Definition for Solver base class.
:copyright: 2020 by nbkode Authors, see AUTHORS for more details.
:license: BSD, see LICENSE for more details.
"""
from __future__ import annotations
import warnings
from abc import ABC, ABCMeta, abstractmethod
from numbers import Real
from typing import Callable, Iterable, Optional, Tuple, Union
import numpy as np
from scipy.integrate._ivp.common import (
select_initial_step,
validate_max_step,
validate_tol,
)
from . import event_handler
from .buffer import AlignedBuffer
from .nbcompat import is_jitted, numba
from .util import CaseInsensitiveDict
class MetaSolver(ABCMeta):
def __repr__(cls):
return f"<{cls.__name__}>"
class Solver(ABC, metaclass=MetaSolver):
"""Base class for all solvers
Parameters
----------
rhs : callable
Right-hand side of the system. The calling signature is ``fun(t, y)``.
Here ``t`` is a scalar, andthe ndarray ``y`` hasna shape (n,);
then ``fun`` must return array_like with shape (n,).
t0 : float
Initial time.
y0 : array_like, shape (n,)
Initial state.
params : array_like
Extra arguments to be passed to the fun as ``fun(t, y, params)``
t_bound : float, optional (default np.inf)
The integration won’t continue beyond this value. Use it only to stop
the integrator when the solution or ecuation has problems after this point.
To obtain the solution at a given timepoint use `run`.
In fixed step methods, the integration stops just before t_bound.
In variable step methods, the integration stops at t_bound.
Attributes
----------
t : float
Current time.
y : ndarray
Current state.
f : ndarray
last evaluation of the rhs.
step_size : float
Size of the last successful step. None if no steps were made yet.
"""
SOLVERS = CaseInsensitiveDict()
SOLVERS_BY_GROUP = CaseInsensitiveDict()
ALIASES = ()
LEN_HISTORY: int = 2
GROUP: str = None
IMPLICIT: bool
FIXED_STEP: bool
#: Callable provided by the user
#: The signature should be (t: float, y: ndarray) -> ndarray
#: or
#: The signature should be (t: float, y: ndarray, p: ndarray) -> ndarray
rhs: Callable
#: user rhs (same as rhs if it was originally jitted and with the right signature)
user_rhs: Callable
#: extra arguments for the user callable
params: np.ndarray or None
#: Last LEN_HISTORY times (ts), states (ys) and derivatives (fs)
cache: AlignedBuffer
#: Classmethods that build steps functions for a particular method.
_fixed_step_builder: Callable
_step_builder: Callable
#: Define which interpolator should be used
#: None -> self._interpolate
#: Other -> other.evaluate
_interpolator = None
def __init__(
self,
rhs: Callable,
t0: float,
y0: np.ndarray,
params: np.ndarray = None,
*,
h: float = None,
t_bound: float = np.inf,
):
self.t_bound = t_bound
if params is not None:
params = np.ascontiguousarray(params)
self.user_rhs = rhs
# TODO: check if it is jitted or njitted. Not sure if this is possible
# if it has not been executed.
if not is_jitted(rhs):
rhs = numba.njit(rhs)
# TODO: A better way to make it partial?
if params is None:
self.rhs = rhs
else:
self.rhs = numba.njit(lambda t, y: rhs(t, y, params))
if h is not None: # It might be set automatically
self.h = np.array(h, dtype=float)
elif not hasattr(self, "h"): # TODO: Make it better.
self.h = 1
t0 = float(t0)
y0 = np.array(y0, dtype=float, ndmin=1)
self.cache = AlignedBuffer(self.LEN_HISTORY, t0, y0, self.rhs(t0, y0))
def __init_subclass__(cls, abstract=False, **kwargs):
"""Initialize Solver subclass by building step methods.
If abstract is True, the class represents a family/group of methods.
If abstract is False, builds cls._fixed_step and cls._step, and adds
the corresponding solver to the SOLVERS_BY_GROUP dictionary.
"""
super().__init_subclass__(**kwargs)
if not abstract:
if not isinstance(cls.LEN_HISTORY, int):
raise ValueError(f"{cls.__name__}.LEN_HISTORY must be an integer.")
elif cls.LEN_HISTORY < 2:
raise ValueError(
f"While defining {cls.__name__}, "
f"LEN_HISTORY cannot be smaller than 1"
)
for name_or_alias in (cls.__name__,) + cls.ALIASES:
if name_or_alias in cls.SOLVERS:
raise Exception(
f"Duplicate name/alias {cls.__name__} in {cls} "
f"collides with {cls.SOLVERS[name_or_alias]}"
)
cls.SOLVERS[name_or_alias] = cls
if cls.GROUP not in cls.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP:
cls.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP[cls.GROUP] = []
cls.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP[cls.GROUP].append(cls)
cls._fixed_step = staticmethod(cls._fixed_step_builder())
step = cls._step_builder()
@numba.njit
def _step(t_bound, rhs, cache, h, *args):
if cache.t + h > t_bound:
return False
else:
step(rhs, cache, h, *args)
return True
cls._step = staticmethod(_step)
@classmethod
@abstractmethod
def _fixed_step_builder(cls):
"""Builds the _fixed_step function of the method."""
@classmethod
@abstractmethod
def _step_builder(cls):
"""Builds the _step function of the method."""
@property
def t(self):
return self.cache.t
@property
def y(self):
return self.cache.y
@property
def f(self):
return self.cache.f
def _check_time(self, t):
if t > self.t_bound:
raise ValueError(
f"Time {t} is larger than solver bound time t_bound={self.t_bound}"
)
def step(self, *, n: int = None, upto_t: float = None) -> Tuple[np.array, np.array]:
"""Advance simulation `n` steps or until the next timepoint will go beyond `upto_t`.
It records and output all intermediate steps.
- `step()` is equivalent to `step(n=1)`
- `step(n=<number>)` is equivalent to `step(n=<number>, upto_t=np.inf)`
- `step(upto_t=<number>)` is similar to `step(n=`np.inf`, upto_t=<number>)`
If `upto_t < self.t`, returns empty arrays for time and state.
Parameters
----------
n : int, optional
Number of steps.
upto_t : float, optional
Returns
-------
np.ndarray, np.ndarray
time vector, state array
Raises
------
ValueError
One of the timepoints provided is outside the valid range.
RuntimeError
The integrator reached `t_bound`.
"""
if upto_t is not None and upto_t < self.t:
return np.asarray([]), np.asarray([])
if n is None and upto_t is None:
# No parameters, make one step.
if self._step(self.t_bound, *self._step_args):
return np.atleast_1d(self.t), self.y
elif upto_t is None:
# Only n is given, make n steps. If t_bound is reached, raise an exception.
ts, ys, scon = self._nsteps(n, self.t_bound, self._step, *self._step_args)
if scon:
raise RuntimeError("Integrator reached t_bound.")
return ts, ys
elif n is None:
# Only upto_t is given, move until that value.
# t_bound will not be reached a it due to validation in _check_time
self._check_time(upto_t)
ts, ys, scon = self._steps(upto_t, self._step, *self._step_args)
return ts, ys
else:
# Both parameters are given, move until either condition is reached.
# t_bound will not be reached a it due to validation in _check_time
self._check_time(upto_t)
ts, ys, scon = self._nsteps(n, upto_t, self._step, *self._step_args)
return ts, ys
def skip(self, *, n: int = None, upto_t: float = None) -> None:
"""Advance simulation `n` steps or until the next timepoint will go beyond `upto_t`.
Unlike `step` or `run`, this method does not output the time and state.
- `skip()` is equivalent to `skip(n=1)`
- `skip(n=<number>)` is equivalent to `skip(n=<number>, upto_t=np.inf)`
- `skip(upto_t=<number>)` is similar to `skip(n=`np.inf`, upto_t=<number>)`
If `upto_t < self.t`, does nothing.
Parameters
----------
n : int, optional
Number of steps.
upto_t : float, optional
Time to reach.
Raises
------
ValueError
One of the timepoints provided is outside the valid range.
RuntimeError
The integrator reached `t_bound`.
"""
if upto_t is not None and upto_t < self.t:
return
if n is None and upto_t is None:
# No parameters, make one step.
self._nskip(1, self.t_bound, self._step, *self._step_args)
elif upto_t is None:
# Only n is given, make n steps. If t_bound is reached, raise an exception.
if self._nskip(n, self.t_bound, self._step, *self._step_args):
raise RuntimeError("Integrator reached t_bound.")
elif n is None:
# Only upto_t is given, move until that value.
# t_bound will not be reached a it due to validation in _check_time
self._check_time(upto_t)
self._skip(upto_t, self._step, *self._step_args)
else:
# Both parameters are given, move until either condition is reached.
# t_bound will not be reached a it due to validation in _check_time
self._check_time(upto_t)
self._nskip(n, upto_t, self._step, *self._step_args)
def run(self, t: Union[Real, np.ndarray]) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""Integrates the ODE interpolating at each of the timepoints `t`.
Parameters
----------
t : float or array-like
Returns
-------
np.ndarray, np.ndarray
time vector, state vector
Raises
------
ValueError
One of the timepoints provided is outside the valid range.
"""
return self.run_events(t, None)[:2]
def run_events(
self,
t: Union[Real, np.ndarray],
events: Optional[Union[Callable, Iterable[Callable]]],
) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""Integrates the ODE interpolating at each of the timepoints `t`.
(events follows the SciPy `solve_ivp` API)
Parameters
----------
t : float or array-like
events : callable, or list of callables (length N)
Events to track. If None (default), no events will be tracked.
Each event occurs at the zeros of a continuous function of time and
state. Each function must have the signature ``event(t, y)`` and return
a float. The solver will find an accurate value of `t` at which
``event(t, y(t)) = 0`` using a root-finding algorithm. By default, all
zeros will be found. The solver looks for a sign change over each step,
so if multiple zero crossings occur within one step, events may be
missed. Additionally each `event` function might have the following
attributes:
terminal: bool, optional
Whether to terminate integration if this event occurs.
Implicitly False if not assigned.
direction: float, optional
Direction of a zero crossing. If `direction` is positive,
`event` will only trigger when going from negative to positive,
and vice versa if `direction` is negative. If 0, then either
direction will trigger event. Implicitly 0 if not assigned.
You can assign attributes like ``event.terminal = True`` to any
function in Python.
Returns
-------
t : ndarray, shape (n_points,)
Time points.
y : ndarray, shape (n, n_points)
Values of the solution at `t`.
t_events : list of ndarray (length N)
Contains for each event type a list of arrays at which an event of
that type event was detected. Empty list if no `events`.
y_events : list of ndarray (length N)
For each value of `t_events`, the corresponding value of the solution.
Empty list if no `events`.
Raises
------
ValueError
One of the timepoints provided is outside the valid range.
"""
t = np.atleast_1d(t).astype(np.float64)
is_t_sorted = t.size == 1 or np.all(t[:-1] <= t[1:])
if not is_t_sorted:
ndx = np.argsort(t)
t = t[ndx]
if t[0] < self.cache.ts[0]:
raise ValueError(
f"Cannot interpolate at t={t[0]} as it is smaller "
f"than the current smallest value in history ({self.cache.ts[0]})"
)
self._check_time(np.max(t))
to_interpolate = t <= self.t
is_to_interpolate = np.any(to_interpolate)
if is_to_interpolate:
t_old = t[to_interpolate]
y_old = np.asarray([self.interpolate(_t) for _t in t_old])
t_to_run = t[np.logical_not(to_interpolate)]
else:
t_to_run = t
# t_bound will not be reached a it due to validation in _check_time
if events:
eh = event_handler.build_handler(events, self.t, self.y)
ts, ys, scon = self._run_eval_events(
self.t_bound,
t_to_run,
self._step,
eh,
self._interpolate,
*self._step_args,
)
# We cast here to a Python List to avoid exposing a Numbatype
t_events = [list(event.t) for event in eh.events]
y_events = [list(event.y) for event in eh.events]
else:
ts, ys, scon = self._run_eval(
self.t_bound,
t_to_run,
self._step,
self._interpolate,
*self._step_args,
)
t_events = []
y_events = []
if is_to_interpolate:
ts = np.concatenate((t_old, ts))
ys = np.concatenate((y_old, ys))
if events:
warnings.warning("Events for past events are not implemented yet.")
if is_t_sorted:
return ts, ys, t_events, y_events
ondx = np.argsort(ndx)
return ts[ondx], ys[ondx], t_events, y_events
def interpolate(self, t: float) -> float:
"""Interpolate solution at t.
This only works for values within the recorded history of the solver.
of the solver instance
Parameters
----------
t : float
Raises
------
ValueError
if the time is outside the recorded history.
"""
# TODO: make this work for array T
if not (self.cache.ts[0] <= t <= self.cache.t):
raise ValueError(
f"Time {t} to interpolate outside range ([{self.cache.ts[0]}, {self.cache.t}])"
)
return self._interpolate(t, *self._step_args)
@staticmethod
@abstractmethod
def _step(t_bound, rhs, cache, h, *args) -> bool:
"""Perform one integration step."""
@property
def _step_args(self):
return self.rhs, self.cache, self.h
@staticmethod
@numba.njit
def _steps(t_end, step, rhs, cache, *args):
"""Step forward until:
- the next step goes beyond `t_end`
The stop condition is in the output to unify the API with
`nsteps`
Returns
-------
np.ndarray, np.ndarray, bool
time vector, state array, stop condition (always True)
"""
t_out = []
y_out = []
while step(t_end, rhs, cache, *args):
t_out.append(cache.t)
y_out.append(np.copy(cache.y))
out = np.empty((len(y_out), cache.y.size))
for ndx, yi in enumerate(y_out):
out[ndx] = yi
return np.array(t_out), out, True
@staticmethod
@numba.njit
def _nsteps(n_steps, t_end, step, rhs, cache, *args):
"""Step forward until:
- the next step goes beyond `t_end`
- `n_steps` steps are done.
Returns
-------
np.ndarray, np.ndarray, bool
time vector, state array, stop condition
Stop condition
True if the integrator stopped due to the time condition.
False, otherwise (it was able to run all all steps).
"""
t_out = np.empty((n_steps,))
y_out = np.empty((n_steps, cache.y.size))
for ndx in range(n_steps):
if not step(t_end, rhs, cache, *args):
return t_out[:ndx], y_out[:ndx], True
t_out[ndx] = cache.t
y_out[ndx] = cache.y
return t_out, y_out, False
@staticmethod
@numba.njit
def _skip(t_end, step, rhs, cache, *args) -> bool:
"""Perform all steps required, stopping just before going beyond t_end.
The stop condition is in the output to unify the API with `nsteps`
Returns
-------
bool
stop_condition (always True)
"""
while step(t_end, rhs, cache, *args):
pass
return True
@staticmethod
@numba.njit
def _nskip(n_steps, t_end, step, rhs, cache, *args) -> bool:
"""Step forward until:
- the next step goes beyond `t_end`
- `n_steps` steps are done.
Returns
-------
np.ndarray, np.ndarray, bool
time vector, state array, stop condition
Stop condition
True if the integrator stopped due to the time condition.
False, otherwise (it was able to run all all steps).
"""
for _ in range(n_steps):
if not step(t_end, rhs, cache, *args):
return True
return False
@staticmethod
@numba.njit()
def _interpolate(t_eval, rhs, cache, *args):
"""Interpolate solution at t_eval.
Does not check that t_eval is valid, that is, that it is not extrapolating.
"""
t0, y0 = cache.ts[0], cache.ys[0]
if t_eval == t0:
return y0
dt, dy = cache.t - t0, cache.y - y0
f0, f1 = cache.fs[0], cache.f
T = (t_eval - t0) / dt
return (
y0
+ T * dy
+ T * (T - 1) * ((1 - 2 * T) * dy + dt * ((T - 1) * f0 + T * f1))
)
@staticmethod
@numba.njit
def _run_eval(
t_bound: float,
t_eval: np.ndarray,
step,
interpolate,
rhs,
cache,
*args,
) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, bool]:
"""Run up to t, evaluating y at given t and return (t, y) as arrays."""
y_out = np.empty((t_eval.size, cache.y.size))
for ndx, ti in enumerate(t_eval):
while cache.t < ti:
if not step(t_bound, rhs, cache, *args):
return t_eval[:ndx], y_out[:ndx], True
y_out[ndx] = interpolate(ti, rhs, cache, *args)
return t_eval, y_out, False
@staticmethod
@numba.njit
def _run_eval_events(
t_bound: float,
t_eval: np.ndarray,
step,
event_handler: event_handler.EventHandler,
interpolate,
rhs,
cache,
*args,
) -> tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, bool]:
"""Run up to t, evaluating y at given t and return (t, y) as arrays."""
y_out = np.empty((t_eval.size, cache.y.size))
for ndx, ti in enumerate(t_eval):
while cache.t < ti:
if not step(t_bound, rhs, cache, *args):
return t_eval[:ndx], y_out[:ndx], True
if event_handler.evaluate(interpolate, rhs, cache, *args):
# Append termination value.
t_eval[ndx], y_out[ndx] = event_handler.last_event
return t_eval[: ndx + 1], y_out[: ndx + 1], True
y_out[ndx] = interpolate(ti, rhs, cache, *args)
return t_eval, y_out, False
variable_step_options = (
"atol",
"rtol",
"min_step",
"max_step",
"min_factor",
"max_factor",
"safety_factor",
)
@numba.jitclass([(s, numba.float64) for s in variable_step_options])
class VariableStepOptions:
def __init__(
self,
atol: float = 1e-6,
rtol: float = 1e-3,
min_step: float = 1e-15,
max_step: float = np.inf,
min_factor: float = 0.2,
max_factor: float = 10.0,
safety_factor: float = 0.9,
):
self.atol = atol
self.rtol = rtol
self.min_step = min_step
self.max_step = max_step
self.min_factor = min_factor
self.max_factor = max_factor
self.safety_factor = safety_factor
class VariableStep:
# instance attributes
first_step: Optional[float]
options: VariableStepOptions
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
self.options = VariableStepOptions(
**{k: kwargs.pop(k) for k in variable_step_options if k in kwargs}
)
h = kwargs.pop("first_step", None)
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
validate_max_step(self.options.max_step)
validate_tol(self.options.rtol, self.options.atol, self.y.size)
if h is None:
h = select_initial_step(
self.rhs,
self.t,
self.y,
self.f,
1,
self.error_estimator_order,
self.options.rtol,
self.options.atol,
)
self.h = np.array(h, dtype=float)
def check(solver, implicit=None, fixed_step=None, runge_kutta=None, multistep=None):
if implicit is not None:
if solver.IMPLICIT is not implicit:
return False
if fixed_step is not None:
if solver.FIXED_STEP is not fixed_step:
return False
if runge_kutta is not None:
from .runge_kutta.core import RungeKutta
if issubclass(solver, RungeKutta) is not runge_kutta:
return False
if multistep is not None:
from .multistep.core import Multistep
if issubclass(solver, Multistep) is not multistep:
return False
return True
[docs]def get_solvers(
*groups, implicit=None, fixed_step=None, runge_kutta=None, multistep=None
):
"""Get available solvers.
Parameters
----------
groups : str
name of the group to filter
implicit : bool
if True, only implicit solvers will be returned.
fixed_step : bool
if True, only fixed step solvers will be returned.
Returns
-------
tuple(Solver)
"""
if not groups:
groups = Solver.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP.keys()
out = []
for group in groups:
try:
out.extend(
filter(
lambda solver: check(
solver, implicit, fixed_step, runge_kutta, multistep
),
Solver.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP[group],
)
)
except KeyError:
m = tuple(Solver.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP.keys())
raise KeyError(f"Group {group} not found. Valid values: {m}")
return tuple(out)
[docs]def get_groups():
"""Get group names."""
return tuple(sorted(Solver.SOLVERS_BY_GROUP.keys()))
_VALID_NAME_ALIAS = None
def list_solvers(
fmt_string="{cls.__name__}",
alias_fmt_string="{name} (alias of {cls.__name__})",
include_alias=True,
):
out = []
for k, v in Solver.SOLVERS.items():
if k == v.__name__:
out.append(fmt_string.format(cls=v, name=k))
elif include_alias:
out.append(alias_fmt_string.format(cls=v, name=k))
return out
def get_solver(name_or_alias):
try:
return Solver.SOLVERS[name_or_alias]
except KeyError:
pass
global _VALID_NAME_ALIAS
if not _VALID_NAME_ALIAS:
_VALID_NAME_ALIAS = "- " + "\n- ".join(sorted(list_solvers()))
raise ValueError(
f"No solver named {name_or_alias}, valid options are:\n{_VALID_NAME_ALIAS}"
)